Updated October 7, 2024 @ 5:09pm
Florida’s storm-battered Gulf Coast raced against a Category 5 hurricane Monday as workers sprinted to pick up heaps of appliances and other street debris left over from Helene two weeks ago and highways were clogged with people fleeing ahead of the storm.
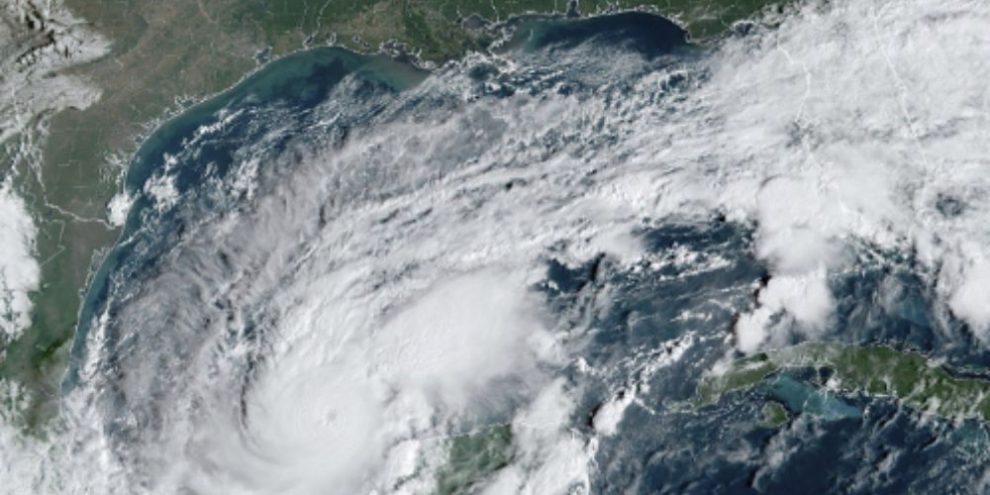
The center of Hurricane Milton could come ashore Wednesday in the Tampa Bay region, which has not endured a direct hit by a major hurricane in more than a century. Scientists expect the system to weaken slightly before landfall, though it could retain hurricane strength as it churns across central Florida toward the Atlantic Ocean. That would largely spare other states ravaged by Helene, which killed at least 230 people on its path from Florida to the Appalachian Mountains.
“This is the real deal here with Milton,” Tampa Mayor Jane Castor told a news conference. “If you want to take on Mother Nature, she wins 100 per cent of the time.”
Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis said Monday that it was imperative that debris from Helene be cleared ahead of Milton’s arrival so the pieces cannot become projectiles.
As evacuation orders were issued, forecasters warned of a possible 8- to 12-foot storm surge (2.4 to 3.6 meters) in Tampa Bay and widespread flooding from 5 to 10 inches (13 to 25 centimetres) of rain in mainland Florida and the Keys. As much as 15 inches (38 centimetres) could fall in places.
The Tampa metro area has a population of more than 3.3 million people.
“It’s a huge population. It’s very exposed, very inexperienced, and that’s a losing proposition,” Massachusetts Institute of Technology meteorology professor Kerry Emanuel said. “I always thought Tampa would be the city to worry about most.”
Much of Florida’s west coast was under hurricane and storm surge watches. A hurricane warning was issued for parts of Mexico’s Yucatan state, which is expected to get sideswiped.
Milton intensified quickly Monday over the eastern Gulf of Mexico. It had maximum sustained winds of 175 mph (282 kph), the National Hurricane Center said. The storm’s center was about 700 miles (1,126 kilometres) southwest of Tampa at midday, moving east-southeast at 9 mph (15 kph).
The Tampa Bay area is still rebounding from Helene and its powerful surge. Twelve people died there, with the worst damage along a string of barrier islands from St. Petersburg to Clearwater.
In the race to clear away the aftermath from Helene, more than 300 vehicles gathered debris Sunday but encountered a locked landfill gate when they tried to drop it off. State troopers used a rope tied to a pickup truck and busted it open, DeSantis said.
“We don’t have time for bureaucracy and red tape,” DeSantis said.
‘It’s going to be flying missiles'
Lifeguards in Pinellas County, on the peninsula that forms Tampa Bay, removed beach chairs and other items that could take flight in strong winds. Elsewhere, stoves, chairs, refrigerators and kitchen tables waited in heaps to be picked up.
Sarah Steslicki, who lives in Belleair Beach, said she was frustrated that more debris had not been collected sooner.
“They’ve screwed around and haven’t picked the debris up, and now they’re scrambling to get it picked up,” Steslicki said Monday. “If this one does hit, it’s going to be flying missiles. Stuff’s going to be floating and flying in the air.”
Hillsborough County, home to Tampa, ordered evacuations for areas adjacent to Tampa Bay and for all mobile and manufactured homes by Tuesday night.
President Biden approved an emergency declaration for Florida, and U.S. Rep. Kathy Castor said 7,000 federal workers were mobilized to help out in one of the largest mobilizations of federal personnel in history.
Barrie's News Delivered To Your Inbox
By submitting this form, you are consenting to receive marketing emails from: Central Ontario Broadcasting, 431 Huronia Rd, Barrie, Ontario, CA, https://www.cobroadcasting.com. You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the SafeUnsubscribe® link, found at the bottom of every email. Emails are serviced by Constant Contact
Reluctance to evacuate
Milton's approach stirred memories of 2017's Hurricane Irma, when about 7 million people were urged to evacuate Florida in an exodus that jammed freeways and clogged gas stations. Some people who left vowed never to evacuate again.
By Monday morning, some gas stations in the Fort Myers and Tampa areas had already run out of gas. Fuel continued to arrive in Florida, and the state had amassed hundreds of thousands of gallons of gasoline and diesel fuel, with much more on the way, DeSantis said.
A steady stream of vehicles headed north toward the Florida Panhandle on Interstate 75, the main highway on the west side of the peninsula, as residents heeded evacuation orders. Traffic clogged the southbound lanes of the highway for miles as other residents headed for the relative safety of Fort Lauderdale and Miami on the other side of the state.
All road tolls were suspended in west-central Florida. State transportation officials allowed motorists to use the left shoulders of northbound Interstate 75 and eastbound Interstate 4 as they evacuated.
Even though Tanya Marunchak’s Belleair Beach home was flooded with more than 4 feet (1.2 meters) of water from Helene, she and her husband were unsure Monday morning if they should evacuate. She wanted to leave, but her husband thought their three-story home was sturdy enough to withstand Milton.
“We lost all our cars, all our furniture. The first floor was completely destroyed,” Marunchak said. “This is the oddest weather predicament that there has ever been.”
Why did Milton intensify so fast?
Milton’s wind speed increased by 92 mph (148 kph) in 24 hours — a pace that trails only those of Hurricane Wilma in 2005 and Hurricane Felix in 2007. One reason Milton strengthened so rapidly is its small “pinhole eye,” just like Wilma's, said Colorado State University hurricane researcher Phil Klotzbach.
The storm will likely go through what’s called an eye wall replacement cycle, a natural process that forms a new eye and expands the storm in size but weakens its wind speeds, Klotzbach said.
The Gulf of Mexico is unusually warm right now, so “the fuel is just there,” and Milton probably went over an extra-warm eddy that helped goose it further, said University of Albany hurricane scientist Kristen Corbosiero.
The last hurricane to be a Category 5 at landfall in the mainland U.S. was Michael in 2018.
Widespread cancellations in Florida
With the storm approaching, schools in Pinellas County, home to St. Petersburg, were being converted into shelters. Officials in Tampa made city garages available to residents hoping to protect their cars from flooding.
Airports in Tampa, St. Petersburg and Orlando planned to close. Walt Disney World said it was operating normally for the time being.
In Mexico, Yucatan state Gov. Joaquín Díaz ordered the cancellation of all nonessential activities except for grocery stores, hospitals, pharmacies and gas stations starting Monday, and Mexican officials organized buses to evacuate residents from the coastal city of Progreso.
It has been two decades since so many storms crisscrossed Florida in such a short period of time. In 2004, an unprecedented five storms struck Florida within six weeks, including three hurricanes that pummeled central Florida.
Other parts of Florida’s Gulf Coast are still recovering from storms. The Fort Myers area in southwest Florida is still rebuilding from Hurricane Ian, which caused $112 billion in damage in 2022. Three hurricanes have thrashed Florida’s Big Bend region in just 13 months, including Helene.
Just 100 feet from the water on Fort Myers Beach, Don Girard was preparing his three-story home for Milton. The home got flooded by Helene two weeks ago and by Debby in August. Two years ago, Hurricane Ian sent waves crashing into the second floor.
“It’s been difficult. I’m not going to lie to you,” Girard said. “The last couple years have been pretty bad.”
___
Schneider reported from Orlando. Associated Press writers Kate Payne in Tampa, Terry Spencer in Fort Myers Beach, Freida Frisaro in Fort Lauderdale, Seth Borenstein in Washington, Brendan Farrington in Tallahassee and Mark Stevenson in Mexico City contributed to this report.